Our science curriculum is built on a knowledge-rich approach, ensuring that students acquire a deep and secure understanding of core scientific concepts and principles. Through carefully sequenced and explicitly taught content, students build the foundational knowledge needed to develop scientific thinking, engage with the natural world meaningfully, and apply what they’ve learned across a range of contexts. This strong knowledge base prepares learners for success in the GCSE Combined Science qualification and supports long-term academic progress in science.
By focusing on a knowledge-rich approach, we ensure that students leave Key Stage 4 not only exam-ready, but scientifically literate—able to understand and question the world around them. Mastery of foundational knowledge enables deeper learning, critical thinking, and success in future STEM pathways.
Our curriculum is ambitious, inclusive, and designed to close knowledge gaps, particularly for disadvantaged learners. By valuing and explicitly teaching scientific knowledge, we empower all students to succeed.
Curriculum Structure
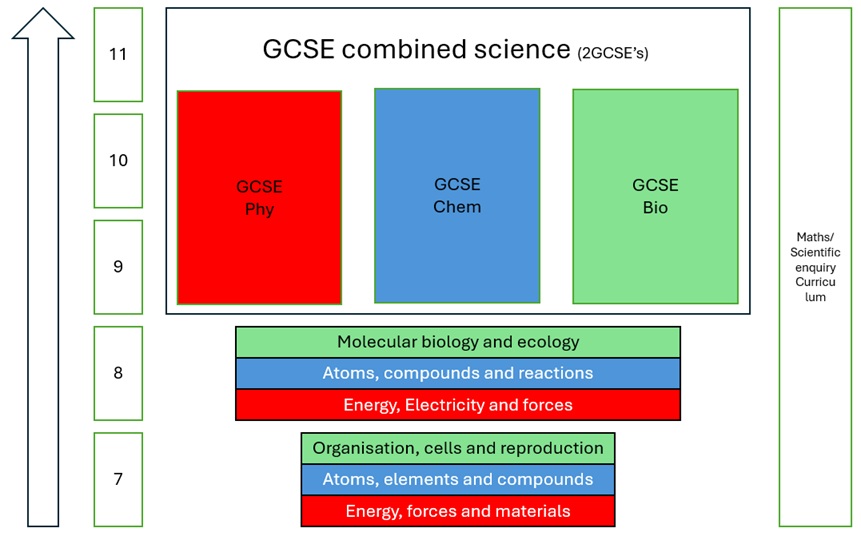
Our five-year science knowledge-curriculum follows a spiral structure, ensuring that key concepts introduced in Year 7 are revisited and developed with increasing depth and complexity in subsequent years. This progressive approach allows students to systematically build a strong foundational understanding, which is then extended and refined in preparation for the study of the GCSE Combined science qualification, which unites Biology, Chemistry, and Physics. The curriculum culminates in the equipping students with the knowledge and skills necessary for success at Key Stage 4 and beyond.
| Year 7 | Year 8 | GCSE Biology | GCSE Chemistry | GCSE Physics |
| Maths in science | Maths in science | Cell biology | Atomic structure and the periodic table | Energy |
| Working scientifically | Energy and electricity | Organisation | Bonding, structure, and the properties of matter | Electricity |
| Energy and forces | Forces and fields | Infection and response | Quantitative chemistry | Particle model of matter |
| Fields and materials | Atomic structure | Bioenergetics | Chemical changes | Atomic structure |
| Discovering the atom | Compounds | Homeostasis and response | Energy changes | Forces |
| Atomic interactions | Chemical interactions | Inheritance, variation and evolution | The rate and extent of chemical change | Waves |
| Organisation of living things | Biological molecules | Ecology | Organic chemistry | Magnetism and electromagnetism |
| Cells and diffusion | Key processes | Chemical analysis | Key ideas | |
| Reproduction | Ecology | Chemistry of the atmosphere | ||
| Using resources |
Curriculum pathway
All students follow the AQA Combined Science: Trilogy course in Key Stage 4. This broad and balanced curriculum covers Biology, Chemistry, and Physics and allows students to achieve up to two GCSEs. It also lays a strong foundation for those who wish to continue studying science beyond GCSE.
For students who show outstanding performance and enthusiasm for science, we offer a Triple Science pathway. This leads to three separate GCSEs—one in each science subject. Entry into Triple Science is based on internal assessments, strong engagement, and a commitment to additional learning time outside the regular timetable. Suitability is discussed with students and families at the start of Year 11.
- Careers visitors e.g. VW group, Jaguar Landrover
- Big bang Fair – Birmingham
- Year 7 Twycross Zoo visit
- Eco-club* (Science links)
- Eureka Science club* starting September 2025

